Meglepő pikkelysömör (psoriasis) tünet enyhülések
Tájékoztatjuk a Tisztelt Érdeklődőket, hogy meglepő tünet enyhüléseket tapasztaltunk pikkelysömör (psoriasis) esetében. A szervezetben lévő zsigeri zsírok gyulladáskeltő hatása is elősegítheti a psoriasis kialakulását, ill. súlyosbíthatja a már kialakult betegség tüneteit. Nemrég meglepő képeket kaptunk arról, milyen eredménnyel járhat apigenin és gyógygomba kivonat keverékek alkalmazása. A képeket most a honlapunkon nyilvánosságra hozzuk. „Gyógygombák/Szakirodalom” menüpontban a „Psoriasis- javulás”.
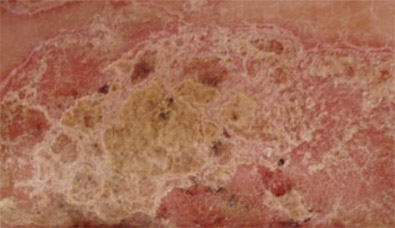
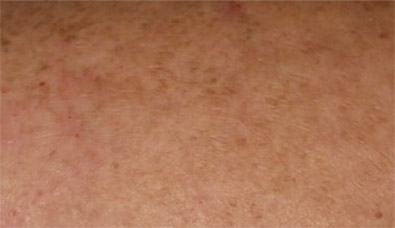
A felső kép a kezelés előtti állapotot ábrázolja, az alsó kép a kb. 4 héttel a kezelés megkezdése utáni állapotot mutatja. Az apigeninről szóló legújabb szakirodalom felhívja a figyelmet arra, hogy a hatóanyag alkalmas lehet a reumás arthritis, a lupus, Crohn betegség kezelésére és a gyulladásos ráktípusok bizonyos halmazának megelőzésére pl. bél és emlő tumoroknál.
A cikkben szereplő megállapítások nem vonatkoztathatóak a honlapon található termékeinkre.
Az angol nyelvű cikket mellékeltük:
Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(2):R59. Epub 2009 Apr 30. Apigenin, a non-mutagenic dietary flavonoid, suppresses lupus by inhibiting autoantigen presentation for expansion of autoreactive Th1 and Th17 cells. Kang HK, Ecklund D, Liu M, Datta SK. Department of Medicine and Microbiology-Immunology, Division of Rheumatology, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, IL 60611, USA. [email protected] Abstract INTRODUCTION: Lupus patients need alternatives to steroids and cytotoxic drugs. We recently found that apigenin, a non-mutagenic dietary flavonoid, can sensitize recurrently activated, normal human T cells to apoptosis by inhibiting nuclear factor-kappa-B (NF-kappaB)-regulated Bcl-xL, cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2), and cellular FLICE-like inhibitory protein (c-FLIP) expression. Because sustained immune activation and hyperexpression of COX-2 and c-FLIP contribute to lupus, we treated SNF1 mice that spontaneously develop human lupus-like disease with apigenin. METHODS: SNF1 mice with established lupus-like disease were injected with 20 mg/kg of apigenin daily and then monitored for development of severe nephritis. Histopathologic changes in kidneys, IgG autoantibodies to nuclear autoantigens in serum and in cultures of splenocytes, along with nucleosome-specific T helper 1 (Th1) and Th17 responses, COX-2 expression, and apoptosis of lupus immune cells were analyzed after apigenin treatment. RESULTS: Apigenin in culture suppressed responses of Th1 and Th17 cells to major lupus autoantigen (nucleosomes) up to 98% and 92%, respectively, and inhibited the ability of lupus B cells to produce IgG class-switched anti-nuclear autoantibodies helped by these Th cells in presence of nucleosomes by up to 82%. Apigenin therapy of SNF1 mice with established lupus suppressed serum levels of pathogenic autoantibodies to nuclear antigens up to 97% and markedly delayed development of severe glomerulonephritis. Apigenin downregulated COX-2 expression in lupus T cells, B cells, and antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and caused their apoptosis. Autoantigen presentation and Th17-inducing cytokine production by dendritic cells were more sensitive to the inhibitory effect of apigenin in culture, as evident at 0.3 to 3 muM, compared with concentrations (10 to 100 microM) required for inducing apoptosis. CONCLUSIONS: Apigenin inhibits autoantigen-presenting and stimulatory functions of APCs necessary for the activation and expansion of autoreactive Th1 and Th17 cells and B cells in lupus. Apigenin also causes apoptosis of hyperactive lupus APCs and T and B cells, probably by inhibiting expression of NF-kappaB-regulated anti-apoptotic molecules, especially COX-2 and c-FLIP, which are persistently hyperexpressed by lupus immune cells. Increasing the bioavailability of dietary plant-derived COX-2 and NF-kappaB inhibitors, such as apigenin, could be valuable for suppressing inflammation in lupus and other Th17-mediated diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn disease, and psoriasis and in prevention of inflammation-based tumors overexpressing COX-2 (colon, breast). PMID: 19405952 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]PMCID: PMC2688212Free PMC Article





